Administration de la gestion de l'eau
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Groups
Years
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
scenario of the flood risk map which shows the floodplain of a modeled 10-year flood event, as demanded by the floods directive 2007/60/EC
-
Typical river restoration technique. Re-meandering and restoration of the riverbed in order to recreate a new meandering course compliant with the river typology, with a riverbed and riverbanks rich in structures.
-
Restoration of the ecological continuity for fish, macroinvertebrates, sediments and terrestrial animals by culverts, through its permanent suppression, or through its adaptation in order to reach natural conditions of substrate, depth, flow rate, luminosity and riverbank structure.
-

Preservation of a corridor for a dynamic river development, where the land is ever not – or extensively used, whose width is compliant with the river typology, which ensures a lateral connection to the alluvial plain, thus creating diversified aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
-
Evaluation of the quality element "hydrological regime" per surface water body
-
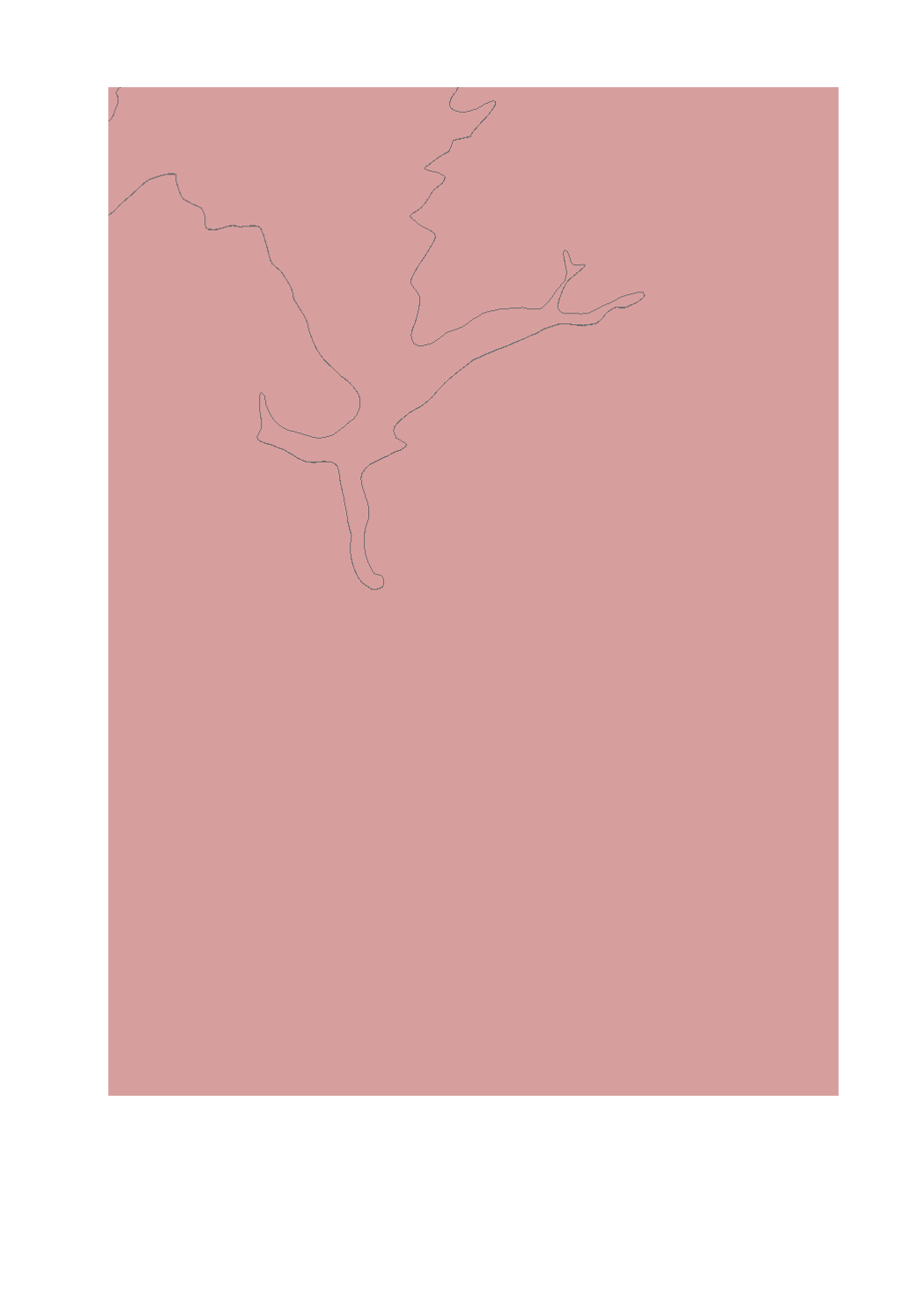

The evaluation of the groundwater bodies is based on the quantitative and the chemical status. The groundwater bodies can be classified as good or as bad.
-
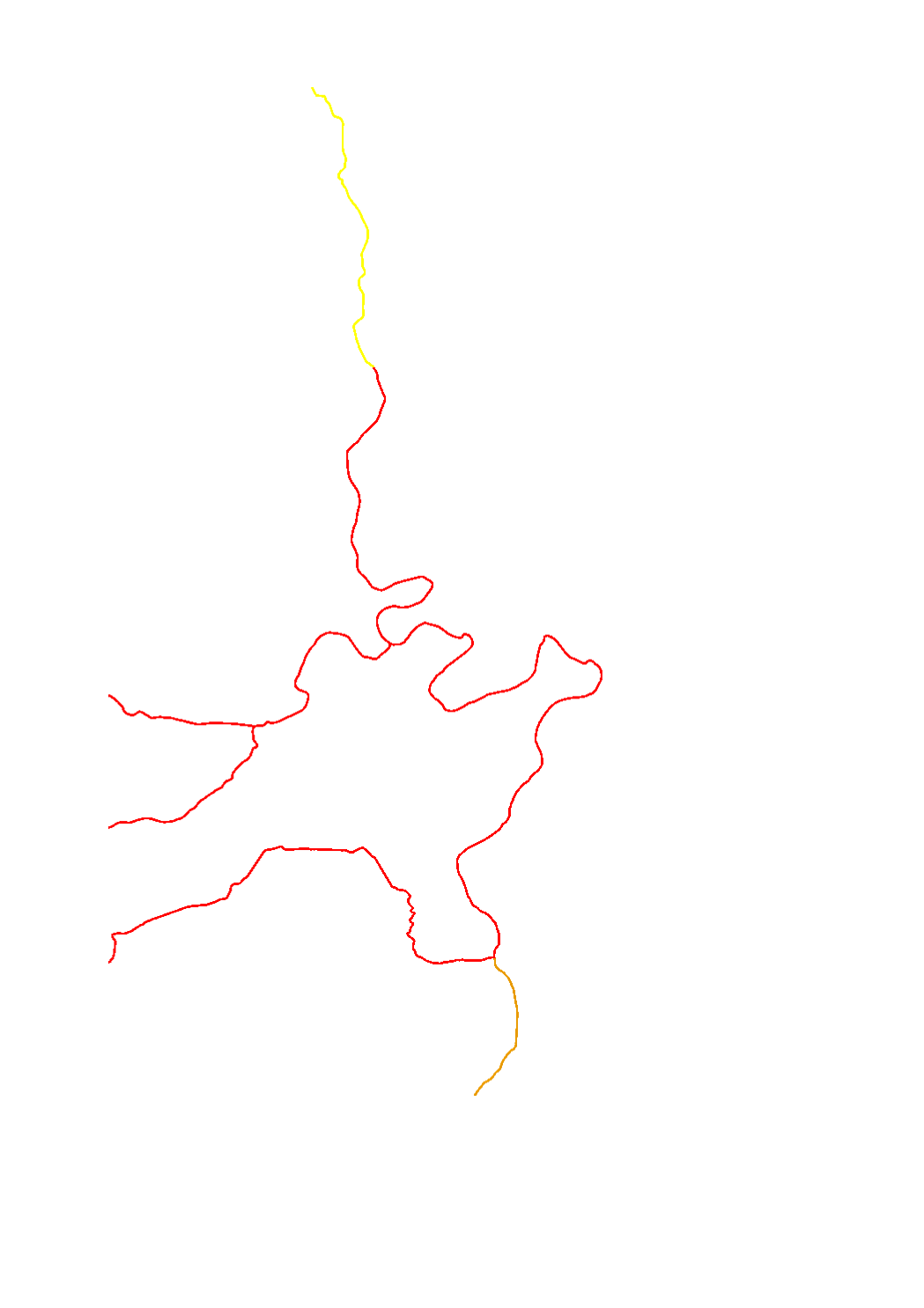
Evaluation of the quality element "continuity" per surface water body
-
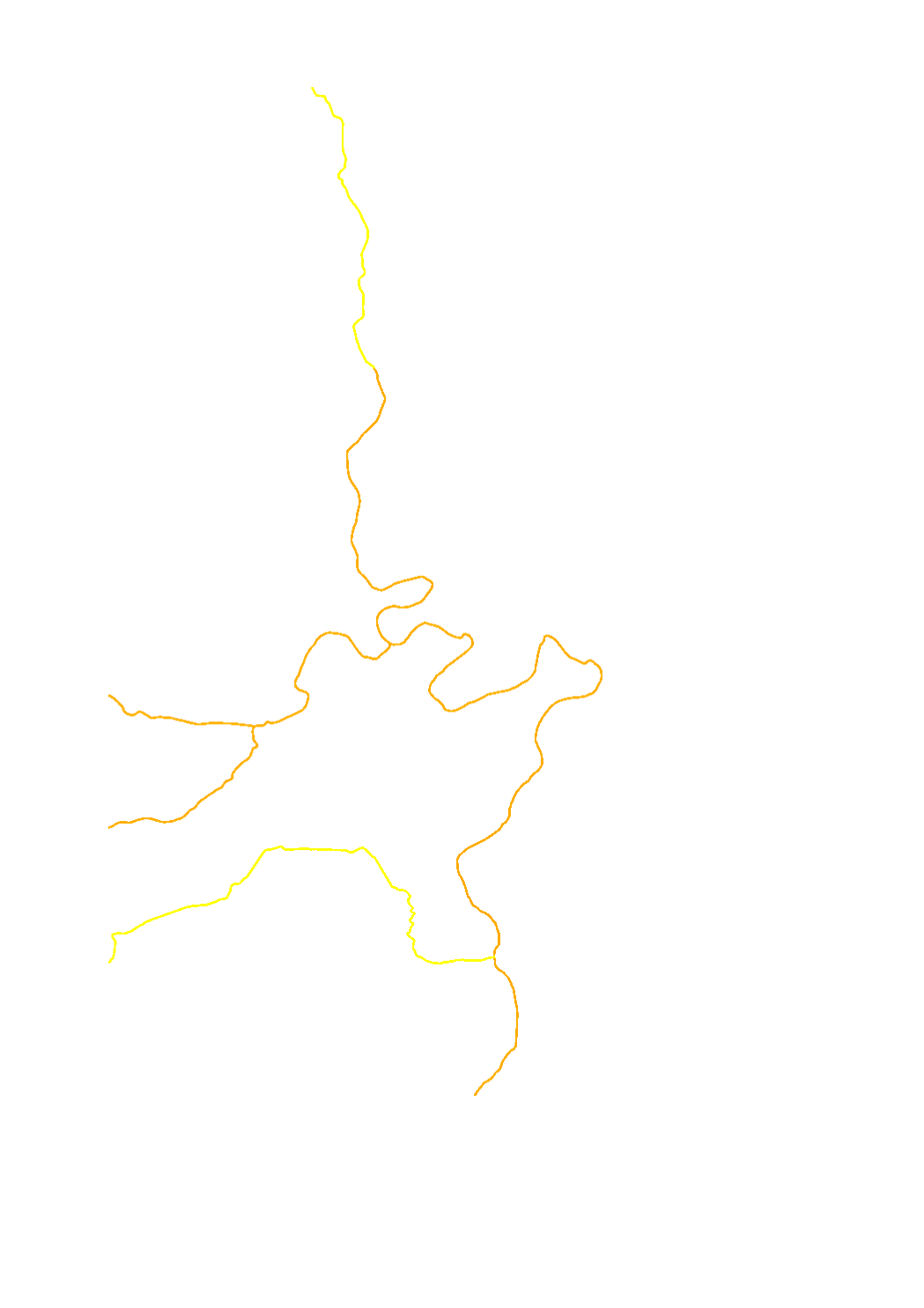
Macrophytes are a sub-element of the biological quality element (BQE) of the aquatic flora used for the assessment of the ecological status/potential. The assessment is made in 5 classes : high (blue) - good (green) - moderate (yellow) - poor (orange) - bad (red). Macrophytes are particularly sensitive to organic pollution, trophy and hydromorphology.
-
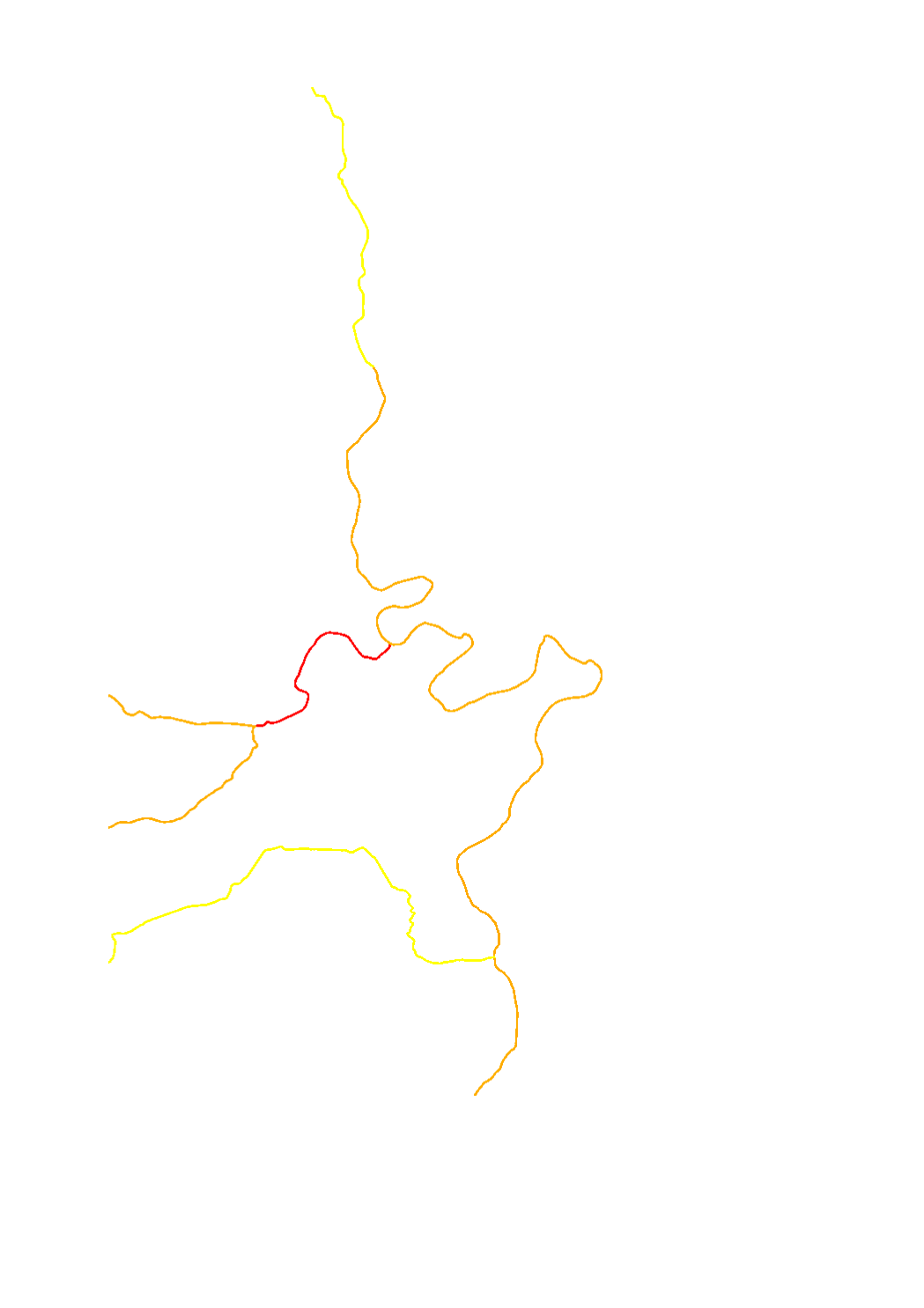
Evaluation of the quality element "morphological conditions" per surface water body
-

The WFD's (2000/60/CE) quantitative status objectives aim to ensure a balance between groundwater withdrawal and recharge.
 geocatalogue.geoportail.lu
geocatalogue.geoportail.lu